• Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a condition in which patients are unable to stop thinking certain thoughts and undertaking particular actions.
Their repetitive behavior greatly interferes with the patient’s normal lifestyle and the daily
life of their family.
• Both serotonin and an increase in the level of glucose metabolism may play a role in this disorder. Cortical regions of the brain have been suggested to be involved in the mediation of the
symptoms.
• Treatments include behavioral
therapies, anxiolytic drugs and antidepressant
(such as the SSRIs, fluoxetine or fluvoxamine(.
• SSRIs increase serotonin
concentration at synapses, which may be responsible for diminishing repetitive behaviors.
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
2/19/2011 |
Posted in
diseases,
nervous system,
notes
|
Read More »
• Chronic renal failure may develop in patients with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus.
• Chronic renal failure is
characterized by heavy
proteinuria,
nausea, tiredness, weakness and abnormal concentrations of creatinine, electrolytes and urea (uraemia) in blood.
There may also be symptoms of headache and neurological changes.
• Loss of albumin in the urine following glomerular
dysfunction causes
oedema, which is often first seen in the
dependent parts of the body, for example ankles.
• Renal failure cause increase in potassium (K+) blood level which leads to muscle weakness and may cause cardiac rhythm disturbance; and decrease in calcium (Ca2+) blood levels which leads to defective mineralization of bones (osteomalacia).
• Renal failure may cause anaemia because of deficient renal secretion
of erythropoietin. Erythropoietin stimulates production of red cells
in bone marrow.
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
2/10/2011 |
Posted in
diseases,
notes,
urinary tract
|
Read More »
• Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease in which the function of the junction between motor nerves and skeletal muscle is affected.
• Myasthenia gravis occur when antibodies attack the acetylcholine receptors at the skeletal neuromuscular junction and therefore acetylcholine fails
to bind to them. The condition results in muscle weakness, particularly of the eye, lips, throat, tongue, neck and
shoulders.
• Movement will be limited when the
limb muscles are affected, making any repetitive action, for example in lifting, running, walking and climbing stairs,
difficult to sustain. Vision will also be affected.
• Drug treatments include the use of anticholinesterase agents (such as
neostigmine and
pyridostigmine) in conjunction with an antimuscarinic drug (such as atropine).
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
2/09/2011 |
Posted in
diseases,
immunology,
muscloskeletal,
nervous system,
notes
|
Read More »

• Anxiety disorder is a condition in
which a state of anxiety persists without any obvious reason.
• The symptoms usually result from overactivity in part of the autonomic nervous system or increased tension in skeletal
muscles.
• The neurotransmitters GABA and serotonin (5-HT) are mainly associated with
anxiety disorders. In addition the sympathetic component of responses is
mediated by noradrenaline.
• Psychological symptoms are: restlessness, worry, tension, irritability, apprehension, depression and fear.
• Somatic symptoms of anxiety are: sleep disturbance, palpitations (increased awareness of the heart
beat, or an irregular heart rhythm), tachycardia, dizziness, breathlessness, blurred vision, dry
mouth, difficulty in swallowing, flatulence, nausea, diarrhea and sweating.
• Treatment includes: non-pharmacological
therapies, such as psychological
approaches,
and pharmacological treatment, use of anxiolytic preparations, such as benzodiazepines, non-benzodiazepines, such as buspirone, and β-adrenoceptor antagonists such as propranolol.
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
2/05/2011 |
Posted in
diseases,
nervous system,
notes
|
Read More »

• Constipation is associated with slow transit of faecal material through the large intestine and
increased fluid absorption, resulting in hard, dry faeces.
• Constipation is common in the elderly, in people with emotional problems or those with an inactive/sedentary lifestyle.
• The main causes
of constipation are: lack
of fiber and fluid in the diet, intestinal muscle weakness and neurogenic disorders.
• Some drugs also can cause constipation such
as:- opiates (as morphine and codeine), calcium channel blocking agents, antacids containing aluminium compounds and
iron salts used in the treatment of
anaemia.
• The main drug treatment for constipation is laxatives. Laxatives are four main types: bulk-forming preparations, hyperosmolar or saline solutions, faecal softeners/ wetting agents and stimulant or irritant laxatives.
• Adverse effects of laxative use or misuse include: flatulence, abdominal distension, cramps and
discomfort, weakness, diarrhoea, dehydration and electrolyte
imbalances.
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
1/24/2011 |
Posted in
diseases,
GIT,
notes
|
Read More »
• Perennial and seasonal allergic
rhinitis are hypersensitivity
reactions
to an allergen.
• Allergens which cause these symptoms include house dust mites, pollens and moulds.
• The symptoms are due to the effects of mast cell degranulation. The effects can cause serious
complications, such as otitis
media
and chronic
sinusitis.
• Treatment of allergic rhinitis includes antihistamines (as chlorpheniramine, loratadine,
cetrizine, and fexofenadine), H1 receptor antagonists (as axelastine) and corticosteroids (as beclometasone and budesonide).
• The first choice treatment for children is cromoglicate.
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
1/19/2011 |
Posted in
diseases,
notes,
respiratory system
|
Read More »
• Depression is characterized by negative, hopeless feelings and feelings of unhappiness for no obvious reason. Patients
may feel worthless; mood,
sleep and energy levels are affected. Depression disturbs many aspects
of our daily
life.
• The depletion of noradrenaline and serotonin stores in the body is believed to
be the underlying pathophysiological explanation.
• Counseling and/or Drug therapy are effective treatments for most
patients. Antidepressant
drugs are three categories: tricyclic
antidepressants, MAOIs and SSRIs.
• The onset of therapeutic responses to antidepressants
delay one- to two-week,
possibly because of the time taken to override feedback mechanisms at nerve endings.
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
1/18/2011 |
Posted in
diseases,
nervous system,
notes
|
Read More »
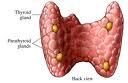
• Hyperparathyroidism results from an
increase in the secretion of PTH (parathyroid hormon).
• The cause in 80% of the
cases is a benign tumour of parathyroid tissue in one of the
glands.
• Hyperparathyroidism leads to bone demineralization and
hypercalcaemia.
• The resultant hypercalcaemia can
also lead to hypophosphataemia, which has deleterious effects on the
cardiovascular, respiratory and muscular systems, leading to general
debility.
• Drug treatments for hyperparathyroidism include the use of
a loop diuretic such as furosemide, biphosphonates and calcitonin.
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
12/06/2010 |
Posted in
diseases,
endocrine system,
notes
|
Read More »
• Symptoms of cystic fibrosis
include secreting of very viscous mucus in the lung and suffering from repeated lung infections.
The pancreas is also affected and patients are deficient in pancreatic
enzymes; this reduces digestion and absorption of nutrients, so affecting growth.
• Patients with cystic fibrosis need physical therapy and
postural drainage to clear the airways because the viscous mucus in cystic
fibrosis is difficult to clear from the lung.
• Sweat glands have sympathetic
cholinergic innervation. Patients with cystic fibrosis secrete a large amount of
salt in their sweat and this forms the basis of a diagnostic test for the
condition.
• Since cystic fibrosis patients lack
digestive enzymes, enzyme preparations containing amylase, lipase and
proteases are prescribed to patients in order to improve intestinal absorption of nutrients.
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
12/05/2010 |
Posted in
diseases,
notes,
respiratory system
|
Read More »
• Lung volumes are changed
differently by restrictive and obstructive disease.
• The main causes of Obstructive lung disease are smoking or prolonged exposure to industrial smokes and
fumes.
• The destruction of lung tissue in emphysema is permanent and
irreversible.
• A trial of corticosteroids and
bronchodilators is recommended because there may be an inflammatory
component in obstructive lung disease,
• Patients with obstructive lung
disease who smoke should quit smoking in order to reduce their
risk of heart disease and to decrease mortality.
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
12/01/2010 |
Posted in
diseases,
notes,
respiratory system
|
Read More »
# General anesthetic drugs are :-
- Inhaled :- * Halothane. * Isoflurane. * Nitrous oxide.
- Intravenous :- * Ketamine. * Propofol.
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
10/16/2010 |
Posted in
drugs,
nervous system,
notes,
pharmacology
|
Read More »
# The drugs which are used for chemothyrapy emesis control are :-
- 5HT3 blockers as Ondansetron & Granisetron.
- Metoclopramide + Corticosteroids.
- Benzodiazepine (Alprazlam & Lorazepam).
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
10/15/2010 |
Posted in
chemothyrapy,
drugs,
notes,
pharmacology
|
Read More »
# Anti-depressant drugs are :-
- Selective seratonin re-uptake inhibitors :-
- Citalopram.
- Escitalopram.
- Fluxetine.
- Paroxetine.
- Tricyclic antidepressants :-
- Amitriptyline.
- Doxepin.
- Imipramine.
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors :-
- Selegiline.
- Prepared by: Dr. Mohamed Abdel Rahman (pharmacist).
- Resources: - Clinical physiology and pharmacology,Farideh Javid and Janice McCurrie 2008.
- Copyrights: All rights are reserved for pharmacist development group 2009 - 2011.
|
10/14/2010 |
Posted in
drugs,
nervous system,
notes,
pharmacology
|
Read More »